Frozen shoulder is a musculoskeletal disorder that manifests itself by severely limiting the mobility of the shoulder joint over time, is painful and negatively affects the quality of life. This condition, called “adhesive capsulitis” in the medical literature, occurs when the capsule surrounding the shoulder joint becomes inflamed, thickened and hardened over time. This process causes both active and passive restriction of joint movements.
It is more common in people over the age of 40 and is known to be slightly more common in women than in men. Some chronic conditions such as diabetes, thyroid diseases and heart diseases are among the major risk factors for developing frozen shoulder. It can also develop after prolonged immobilization, shoulder trauma or surgical interventions.
Early diagnosis and personalized treatment process are of great importance in the treatment of frozen shoulder. Approaches such as physical therapy applications, exercise programs, medical treatment and in some cases injections are evaluated together, aiming to return the patient to daily life and regain joint functions.
Table of Contents
- What is Frozen Shoulder?
- What Causes Frozen Shoulder?
- Symptoms of Frozen Shoulder
- Frozen Shoulder Treatment Methods
- Frozen Shoulder Exercises
- Frozen Shoulder Syndrome
- Surgical Options in Frozen Shoulder
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Conclusion
What is Frozen Shoulder?
Frozen shoulder, medically known as adhesive capsulitis, is a musculoskeletal disorder characterized by severe limitation of movement and pain caused by thickening, narrowing and adhesions in the capsular tissue of the shoulder joint. The shoulder joint is a complex structure between the upper arm bone (humerus), shoulder blade (scapula) and collarbone (clavicle). This joint is surrounded by a capsule of connective tissue. In frozen shoulder, this capsule thickens and hardens and adhesions form within the joint, restricting movement.
The disease usually progresses in three stages:
- Painful Phase (Freezing Phase): Pain in the shoulder gradually increases and can become severe enough to disturb night sleep. During this period, range of motion begins to be restricted.
- Frozen Phase: The pain is stabilized or relieved, but the limitation of movement becomes more pronounced. The person begins to experience serious difficulties in activities of daily living.
- Thaw Phase: In this phase, shoulder mobility is gradually restored. However, this process takes months and in some cases even years.

Frozen shoulder is mostly seen in people between the ages of 40 and 60 and is more common in women than in men. It usually affects only one shoulder. Conditions such as diabetes, thyroid disorders, heart diseases and prolonged immobility can trigger the development of frozen shoulder. In addition, trauma to the shoulder area, surgery or immobilization also increase the risk.
At the onset of the disease, an insidious pain is usually observed. Over time, this pain intensifies and becomes more pronounced as the shoulder is moved. After a while, the person starts to have difficulty lifting the arm upwards, extending it towards the back or even doing simple daily tasks. In advanced cases, the person is almost unable to use the shoulder at all.
What Causes Frozen Shoulder?
Although the mechanisms involved in the development of frozen shoulder have not been fully elucidated, it is known that many risk factors trigger this condition. Inflammation of the capsular tissue surrounding the shoulder joint and the resulting adhesions lead to restricted movement and severe pain. Some of the main factors that trigger this process are listed below:
- Restriction of movement after shoulder surgery causes the capsular tissue not to stretch sufficiently and harden over time. This becomes even more evident when the shoulder is not mobilized sufficiently in the postoperative period.
- Suspension of the arm after traumas such as fracture or dislocation facilitates the formation of adhesions in the shoulder joint capsule with prolonged immobilization. This leads to loss of the natural range of motion of the joint.
- The presence of diabetes and thyroid diseases have negative effects on connective tissue, disrupting the structural integrity of the capsule and accelerating the development of frozen shoulder. Especially in individuals with diabetes, the incidence of frozen shoulder is significantly higher than in the general population.
- The presence of systemic disorders such as heart diseases negatively affects blood circulation and the healing capacity of connective tissue, facilitating the development of inflammation and fibrosis in the shoulder capsule.
- Sudden falls, bumps or blows to the shoulder area initiate an inflammatory process by causing micro-level damage to the capsular tissue and this process can turn into a frozen shoulder picture over time.
Symptoms of Frozen Shoulder
Frozen shoulder is a disease that progresses slowly but its effects are quite pronounced. It usually progresses in three main stages, with symptoms of varying severity at each stage. Throughout the process, patients’ quality of life is significantly reduced and daily activities are severely restricted.
A. Freezing (Painful) Stage
In the first stage, he or she feels a gradually increasing pain in the shoulder area. This pain usually starts insidiously and intensifies over time. Especially at night, the pain becomes more pronounced and reaches a level that can wake you up from sleep. When the arm is tried to be moved, a stinging or burning discomfort sensation occurs. Patients tend to protect their shoulders and avoid movement during this period.
B. Frozen Stage
At this stage, the pain loses some of its intensity. However, the limitation of movement becomes more prominent. The shoulder joint starts to stiffen. There are severe limitations in both active (self-initiated) and passive (assisted) movements. The person is unable to raise his/her arm upwards, reach it behind the back or perform simple daily tasks. Even simple activities such as getting dressed, combing one’s hair, or reaching into one’s back pocket can become difficult. These everyday tasks may pose a great challenge.
C. Thawing (Recovery) Phase
In the final stage, the symptoms gradually begin to ease. The adhesions in the joint capsule dissolve over time, the range of motion of the shoulder increases and the pain decreases. However, this process takes months and in some cases years. Physical therapy and regular exercises accelerate the healing process at this stage.

Common Symptoms of Frozen Shoulder
- Frozen shoulder is characterized by a number of specific symptoms. These symptoms are felt at different intensities over time and may vary depending on the stage of the disease:
- Waking up at night due to pain. The pain, which increases especially when lying on the shoulder, often wakes patients from sleep and reduces the quality of sleep.
- Constant pain in the shoulder. Pain, especially in the anterior, outer or deeper parts of the shoulder, increases with movement and may persist even during rest.
- The arm cannot be raised to the overhead position. When upward movements such as reaching for shelves, hanging curtains, or lifting hands are attempted, the shoulder becomes restricted. This restriction leads to difficulty and discomfort. Shoulder stiffness and pain prevent these actions.
- Daily movements such as dressing and combing hair are difficult. The inability of the shoulder to fulfill its daily functions has a significant impact. It negatively affects the person’s ability to live independently.
Frozen Shoulder Treatment Methods
Treatment of frozen shoulder is planned with an individualized approach. It takes into account the stage of the disease and the general health status of the patient. The aim of the treatment process is to relieve pain in the shoulder joint. It also focuses on increasing range of motion and restoring the patient’s quality of life.
- Drug Therapy
In the first stage, medication is used to control the inflammation caused by the disease and reduce pain.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are used to reduce pain and control inflammation.
- When necessary, muscle relaxants are also prescribed to relieve muscle spasms.
This treatment approach is especially preferred during the freezing phase of the disease. It is used to control the intense pain felt at this stage.
- Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
One of the most basic steps in the treatment of frozen shoulder is physical therapy. Through exercise programs led by a specialist physiotherapist:
- The flexibility of the shoulder capsule is increased,
- Muscle tissues are strengthened,
- Joint range of motion is restored.
Physical therapy applications include techniques such as hot and cold compresses, ultrasound therapy, electrical stimulation. In addition, stretching and mobilization exercises form the basis of the process. These exercises require the active participation of the patient.
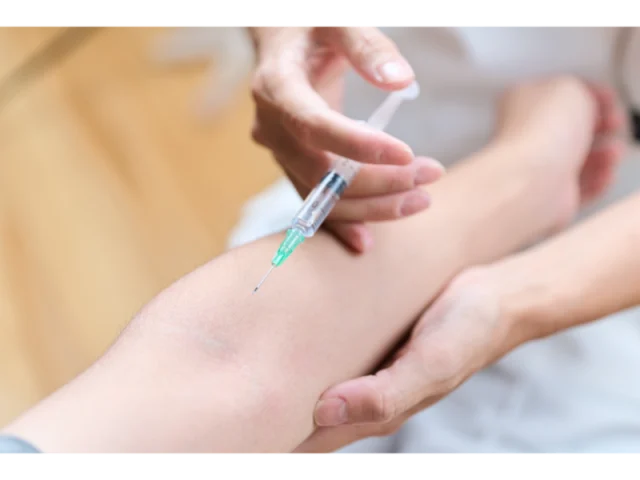
- Steroid Injections
Intra-articular corticosteroid injections are preferred in cases of intense pain. They are especially useful when the pain makes it difficult to start physical therapy.
- The injection rapidly reduces inflammation,
- It relieves pain and facilitates the transition to physical therapy.
- Manipulation (Manipulation under anesthesia)
In patients with severe limitation of movement, other treatments may not be effective. In such cases, manipulation is performed under general anesthesia.
- The patient is given anesthesia.
Frozen Shoulder Exercises
One of the most effective and indispensable components of frozen shoulder treatment is regular exercise. Exercise programs aim to restore the range of motion of the shoulder joint. They also help strengthen muscle tissue and reduce pain.
When these exercises are performed regularly, the healing process accelerates. Shoulder function is gradually restored over time.
Below are some basic exercises that are often recommended in the treatment of frozen shoulder:
- Arm drooping movement (Pendulum exercise)
This exercise helps to increase range of motion. It does so without placing a direct load on the shoulder joint.
- The patient leans slightly forward, the healthy arm is supported by leaning against something.
- The uncomfortable arm is freed and lowered downwards under the influence of gravity.
- The arm is swung clockwise and counterclockwise in small circles for 10-15 repetitions.
This exercise relaxes the muscles and acclimatizes the shoulder capsule to movement without straining it.
2. Wall Climbing Exercise
This exercise, which promotes upward movement of the shoulder, is often recommended for frozen shoulder.
- Standing with the face facing the wall.
- The fingertips touch the wall. Walk upwards like a spider.
- The arm is advanced until it reaches the highest possible point, then slowly lowered down. This movement stretches the shoulder capsule and increases the range of motion.
3. Active Elbow Flexion/Extension
This exercise aims to promote arm movement while keeping the shoulder stationary.
- The patient sits or stands.
- The shoulder is fixed and only the elbow joint is moved.
- The arm is bent at the elbow and unbent again for 10-15 repetitions. This exercise both increases circulation and helps to mobilize the muscles around the shoulder.

Frozen Shoulder Syndrome
This syndrome (adhesive capsulitis) is a condition characterized by stiffness and increasing pain in the shoulder joint. It typically develops gradually and progresses through three stages: the freezing stage, the frozen stage, and the thawing stage. Each phase can last for several months.
Common symptoms include persistent shoulder pain, restricted range of motion, and discomfort that may disrupt sleep, especially at night. It is most commonly seen in individuals over the age of 40 and is often associated with chronic conditions like diabetes.
Early diagnosis and physical therapy can significantly reduce the risk of long-term stiffness. Treatment usually involves therapeutic exercises, physical therapy, pain relievers, and in some cases, corticosteroid injections.
Surgical Options in Frozen Shoulder
If pain and limitation persist despite physical therapy and medications, surgical intervention may be required. The shoulder capsule is released with arthroscopic capsular release method. After this operation, patients can usually return to their daily lives in a short time.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Will frozen shoulder go away on its own?
Some cases improve over time. However, medical intervention and exercise are usually necessary.
How long does it take for frozen shoulder to heal?
The healing process can vary between 12-24 months.
Is physical therapy necessary?
Yes. Exercise therapy plays a critical role. It helps restore the shoulder to its former range of motion.
When is frozen shoulder surgery necessary?
Surgery should be considered if there is no response to medication and exercises.
Is every shoulder pain a frozen shoulder?
No, it is not. Frozen shoulder has its own stages and symptoms. An orthopedic specialist should be consulted for an accurate diagnosis.
Conclusion
Frozen shoulder is an important musculoskeletal disorder. It causes pain and limitation of movement in the shoulder joint. It directly affects activities of daily living. If not recognized in time, this condition can lead to long-term loss of movement. It also causes a significant decrease in quality of life. However, early diagnosis plays a major role in stopping the progression of the disease. It also significantly increases the effectiveness of the treatment process.
In the treatment process, shoulder functions can be restored to a great extent. This is achieved through individually planned physical therapy applications. Regular exercise programs and, when necessary, medical or surgical interventions further support recovery. Exercises are one of the most critical steps in the healing process. Their effectiveness increases significantly when performed with patience and discipline.
Adopting a multidisciplinary approach in the treatment of frozen shoulder ensures effective pain control. It also helps restore joint mobility. This process, carried out with expert support, helps manage pain effectively. It allows patients to step into a functional and healthy life.

















 Youtube Videolarım
Youtube Videolarım




