Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries are among the most common and serious conditions threatening knee health. They often occur during sudden changes in direction, jumping, or unbalanced falls.
This type of injury affects not only professional athletes but also anyone who leads an active lifestyle. It typically presents with symptoms such as loss of stability in the knee, intense pain, swelling, and limited mobility.
With early diagnosis and the right treatment approach, both pain can be managed and knee function can be restored. In this article, we explore the causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and effective treatment strategies for ACL injuries.
By doing so, we provide all the essential information you need to protect your knee health and improve your quality of life.
Table of Contents
- Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Injury
- Symptoms of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tear
- Symptoms of Posterior Cruciate Ligament Tear
- Symptoms of Collateral Ligament Tear
- Causes of Cruciate Ligament Injuries
- Treatment of Cruciate Ligament Injuries
- Surgical Intervention and Postoperative Rehabilitation
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Conclusion
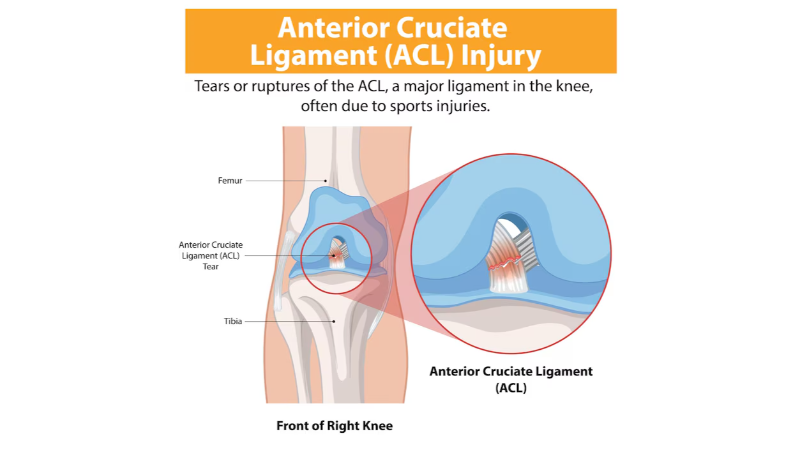
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Injury
Cruciate ligament tears are common soft tissue injuries in the knee joint that significantly affect mobility. These ligaments connect the femur (thigh bone) to the tibia (shin bone). They allow the knee to move in the correct axis during motion. They are essential for maintaining knee joint stability. This is especially true during sudden directional changes, jumping, or abrupt stopping movements.
Cruciate ligaments are categorized into anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), and collateral ligaments. When any of these ligaments tear, the stability of the knee is compromised. This condition does not only affect professional athletes. It can also lead to serious mobility limitations in physically active individuals in daily life.
Cruciate ligament injuries are most often caused by sports-related trauma. However, they can also result from falls, direct blows, or sudden overexertion.

Symptoms of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tear
Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tears are serious knee injuries. They are particularly common in sports that involve sudden changes in direction, such as football, basketball, and skiing. These injuries significantly affect knee stability. They restrict movement. Daily activities become more difficult.
When the ACL tears, a sudden and intense pain is usually felt in the knee at the moment of trauma. This pain often forces the person to stop moving immediately. A “pop” sound may be heard inside the knee. It is often described as a tearing or snapping noise.
A noticeable swelling develops in the knee within a short time. This swelling typically occurs due to bleeding within the ligament spreading into the joint space. A sensation of instability is one of the most prominent symptoms of an ACL tear. Patients often feel the knee giving way. This causes the person to lose control of the knee while walking or climbing stairs.
Pain increases during walking. And it becomes difficult to bear full weight on the knee. For this reason, individuals with an ACL tear experience significant limitations in daily activities. If not diagnosed early, this condition can lead to long-term damage to the meniscus or cartilage.
Symptoms of Posterior Cruciate Ligament Tear
Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) tears are less common than anterior cruciate ligament injuries. However, they can occur especially after high-energy trauma. Damage to this ligament negatively affects the load-bearing function of the back of the knee. It also impairs the knee’s ability to maintain balance. Although the symptoms are often mild, certain signs can be clearly observed when carefully evaluated:
- Loss of balance and a sense of instability:
Although not always prominent, some patients with a PCL tear experience balance issues. These issues are due to the knee shifting forward. This becomes more noticeable during athletic movements. - Mild pain and swelling:
Pain in PCL tears is typically felt at the back of the knee and is mild in the early stages. Swelling may develop within the first 24 hours following trauma. This is caused by an increase in joint fluid due to the ligament tear. - Loss of knee stability:
The PCL is one of the main structures that prevent the knee from sliding forward. When the ligament is torn, a feeling of looseness occurs in the knee. This increases the risk of losing control during everyday movements. - Difficulty climbing stairs:
Movements such as going uphill or climbing stairs cause a noticeable feeling of insecurity and strain in the knee. During such actions, the patient realizes that the leg does not provide strong enough support. - Pain in the back of the knee:
Pain often concentrates in the posterior part of the knee. Increased pressure in this area leads to discomfort while sitting or squatting. It also causes discomfort when the knee is kept bent for long periods.
Symptoms of Collateral Ligament Tear
The collateral ligaments are located on the inner (medial) and outer (lateral) sides of the knee. They are key structures that provide lateral stability to the joint. Tears in these ligaments usually occur due to sprains or sudden changes in direction. They can also result from direct impact. The injury results from excessive stress forcing the knee inward or outward. It significantly affects both daily life and athletic activities.
The main symptoms observed in the event of a tear include:
- Pain on the sides of the knee:
After the injury, pain becomes concentrated on either the inner or outer side where the ligament is located. This pain intensifies when pressure is applied and becomes more noticeable during movement. Tenderness is especially felt on the side where the ligament is torn. - Difficulty standing upright:
When one of the collateral ligaments is torn, the knee loses its stability. This makes it difficult for the patient to maintain balance while standing. It also prevents even distribution of body weight. It leads to a sense of insecurity while standing. - Sideways shifting of the knee:
As the ligament can no longer fulfill its function, the knee loses control during lateral movements. Patients often describe this as a feeling of the knee “giving way to the side.” Others refer to it as “slipping.” - Instability during exercises:
When exercising or playing sports, the knee may not provide adequate support. This can cause imbalance during movements. This is especially noticeable in side steps or turns. As a result, athletic performance declines and the risk of further injury increases.
Causes of Cruciate Ligament Injuries
Cruciate ligaments are essential structures that stabilize the knee joint. They ensure proper movement alignment during activity. These ligaments can tear as a result of specific trauma or excessive strain. Ligament tears are frequently seen in both professional athletes and individuals with active daily lives. The injuries usually occur due to sudden and uncontrolled movements.
The main causes of ligament tears include:
- Sudden change of direction:
A sudden change in direction during sports or exercise puts significant stress on the knee joint. Especially when the foot remains planted while the upper body rotates. This sudden load on the cruciate ligaments can lead to a tear. - Improper landing or jumping:
Landing incorrectly after jumping from a height can push the joint beyond its natural range of motion. In such cases, the ligaments are overstretched, increasing the risk of tearing. - Direct impact:
A direct blow to the knee joint causes the ligaments to stretch suddenly and unevenly. Such impacts are commonly seen in contact sports, falls, or collisions. - Motor vehicle accidents:
In high-energy traumas like traffic accidents, a forceful impact to a bent knee can result in a cruciate ligament tear. These types of injuries often affect the posterior cruciate ligament. - Knee strain in contact sports like football or basketball:
Frequent sudden stops, turns, and collisions in contact sports cause unnatural knee movements. This is one of the leading causes of anterior cruciate ligament injuries.
Treatment of Cruciate Ligament Injuries
The treatment is tailored to the individual based on the patient’s age and activity level. The severity of the injury is also taken into account. Therefore, before starting treatment, a thorough physical examination must be performed. Appropriate imaging techniques should also be used to clearly assess the extent of the ligament damage. With the right treatment approach, knee stability is preserved. The patient’s quality of life is also improved.
The main approaches followed during the treatment process include:
- Physical therapy is sufficient in mild cases:
Partial ligament injuries or incomplete tears usually do not require surgical intervention. In such cases, physical therapy programs are used to strengthen the muscles around the knee. Supporting the muscular structure helps maintain knee stability. And the individual can return to normal activities more quickly. - Knee braces and protective equipment should be used in moderate injuries:
Supportive knee braces prevent excessive movement of the knee and aid the healing process. Especially in athletes, activity restriction is combined with supportive equipment. This helps prevent the progression of the injury. It also contributes to pain relief. - Surgical intervention is necessary in severe cases:
Complete tears or injuries that cause significant instability in the knee make surgical treatment inevitable. Cruciate ligament reconstruction, usually performed using arthroscopic methods, enables the torn ligament to be rebuilt. Post-surgery, a physical therapy program gradually restores knee function.
Surgical Intervention and Postoperative Rehabilitation
Surgical intervention in cruciate ligament tears is especially preferred in the presence of complete ruptures. It also stands out as a permanent solution when there is significant instability in the knee. In surgical treatment, the torn ligament is reconstructed using a special graft. This procedure is usually performed arthroscopically, meaning with minimally invasive techniques. This makes the recovery process more comfortable and reduces the risk of infection.
The rehabilitation period is just as critical to treatment success as the recovery after surgery. The following practices play a key role during this phase:
- Rest and cold application in the first weeks:
Immediately after surgery, avoiding strain on the knee is necessary to reduce swelling and control pain. Cold applications help relieve swelling and provide comfort to the patient. During this period, the knee should be protected from load. It should be kept at rest as much as possible. - Controlled physical therapy programs:
In the following weeks of healing, guided exercises with a specialized physiotherapist are introduced.
These exercises help keep the surrounding muscles active. Range of motion and balance exercises are gradually increased under supervision. Sudden or strenuous movements must be avoided. - Exercises to strengthen the muscles:
Over time, weakening of the muscles around the knee may disrupt joint stability. Therefore, strengthening exercises targeting the quadriceps and hamstrings are of great importance. These exercises help the knee become more stable and reduce the risk of reinjury. - Therapy sessions to restore knee mobility:
One of the primary goals of rehabilitation is to restore the knee’s flexibility and range of motion. For this purpose, passive and active range of motion exercises are performed. Therapy should continue until full bending and extension of the knee is regained.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How long does it take for an ACL tear to heal?
Full recovery can be achieved within 6–9 months after surgery. The physical therapy process contributes significantly to this.
Can a cruciate ligament tear heal without surgery?
In mild injuries, physical therapy may be sufficient. However, surgery is recommended in cases of severe tears.
Can sports be resumed after cruciate ligament surgery?
But a controlled return should be made. This must follow the rehabilitation program set by the doctor.
Do cruciate ligament tears only happen to athletes?
No. They can occur in everyday life as well, due to falls or traumatic incidents.
Can a cruciate ligament tear be clearly seen on an MRI scan?
Yes. MRI is one of the most reliable imaging methods for detecting such injuries.
Conclusion
Cruciate ligament tears are common injuries, especially among individuals with active lifestyles. This condition significantly affects knee mobility and daily functionality. Although frequently seen in athletes, it can occur in people of all ages. This may happen due to falls, impacts, or sudden movements. When identified early and treated correctly, such injuries can be completely managed.
If symptoms such as pain, swelling, a feeling of looseness, or instability in the knee are observed, caution should be exercised. In such cases, it is extremely important to consult an orthopedic specialist without delay. Starting treatment early ensures faster recovery. It also helps prevent long-term complications.
There are mild cases that can be managed without surgery. In more severe situations requiring surgical intervention, effective treatment options are also available. When the rehabilitation process is followed properly, patients can largely regain the function of their knees.
Anterior cruciate ligament is a treatable condition with accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment approaches. Symptoms should never be ignored in order to protect a healthy knee structure. For safe mobility, professional medical support must always be sought.
Don’t forget to visit our blog to explore more topics on orthopedics and joint health!


















 Youtube Videos
Youtube Videos




